Git guides
Make changes in a repository
Git workflow
| It is best practice to check for changes on remote before changing files locally and before pushing changes to remote. |
The Git workflow for making changes is a 4 step process:
-
Make the changes in your working copy.
-
Add files from the working copy to the staging area (
git add). -
Commit staged files to your local repo (
git commit). -
Push to a remote repository (
git push).
Cloning a repository
If you want to work on a repository locally, you need to first check it out from remote (GitLab). To do so, follow one of the cloning instructions below.
| If your project contains submodules, make sure to also update them. |
-
Find the repository url on the website and copy the git url
-
Open the folder on your PC where you want to save the repository
-
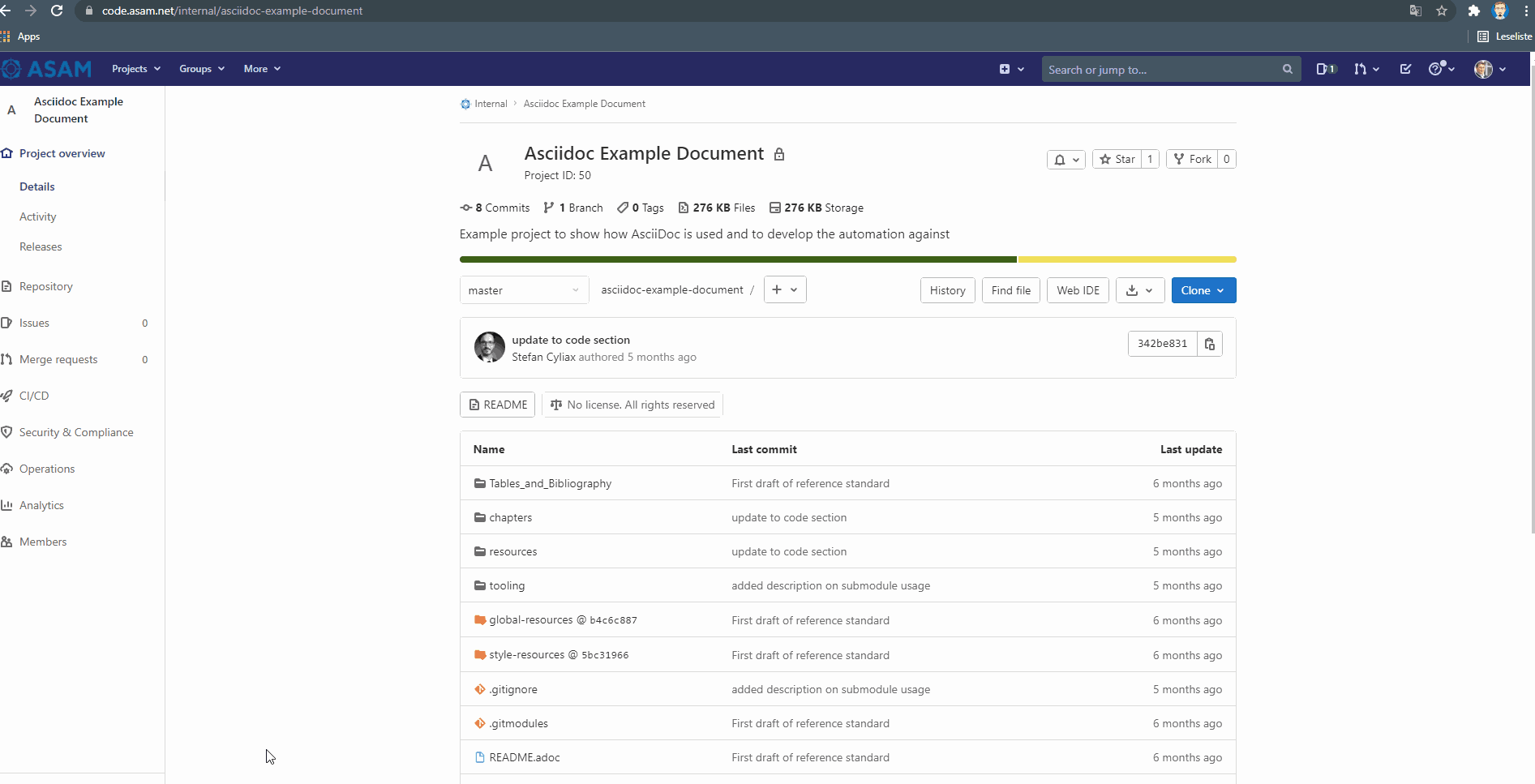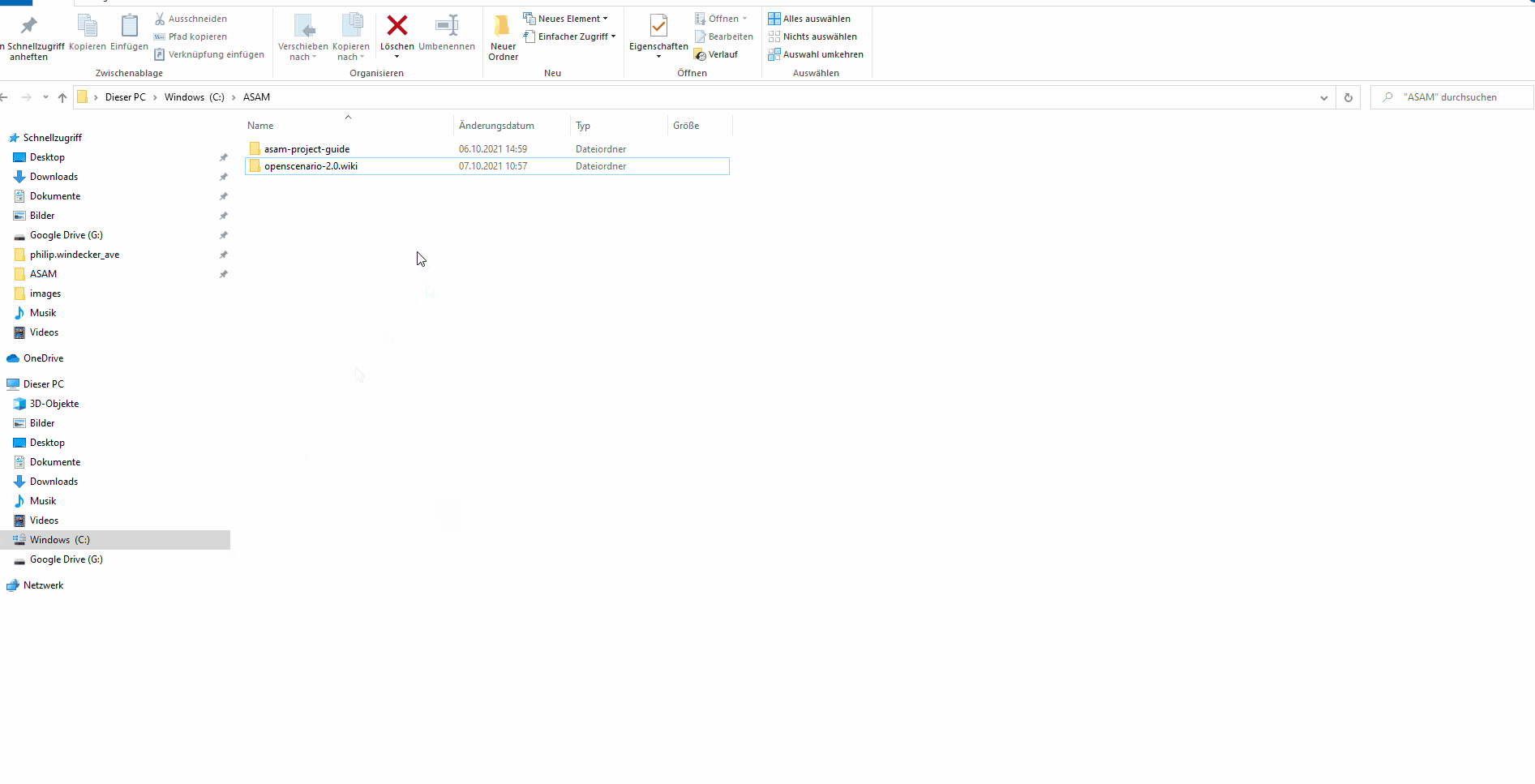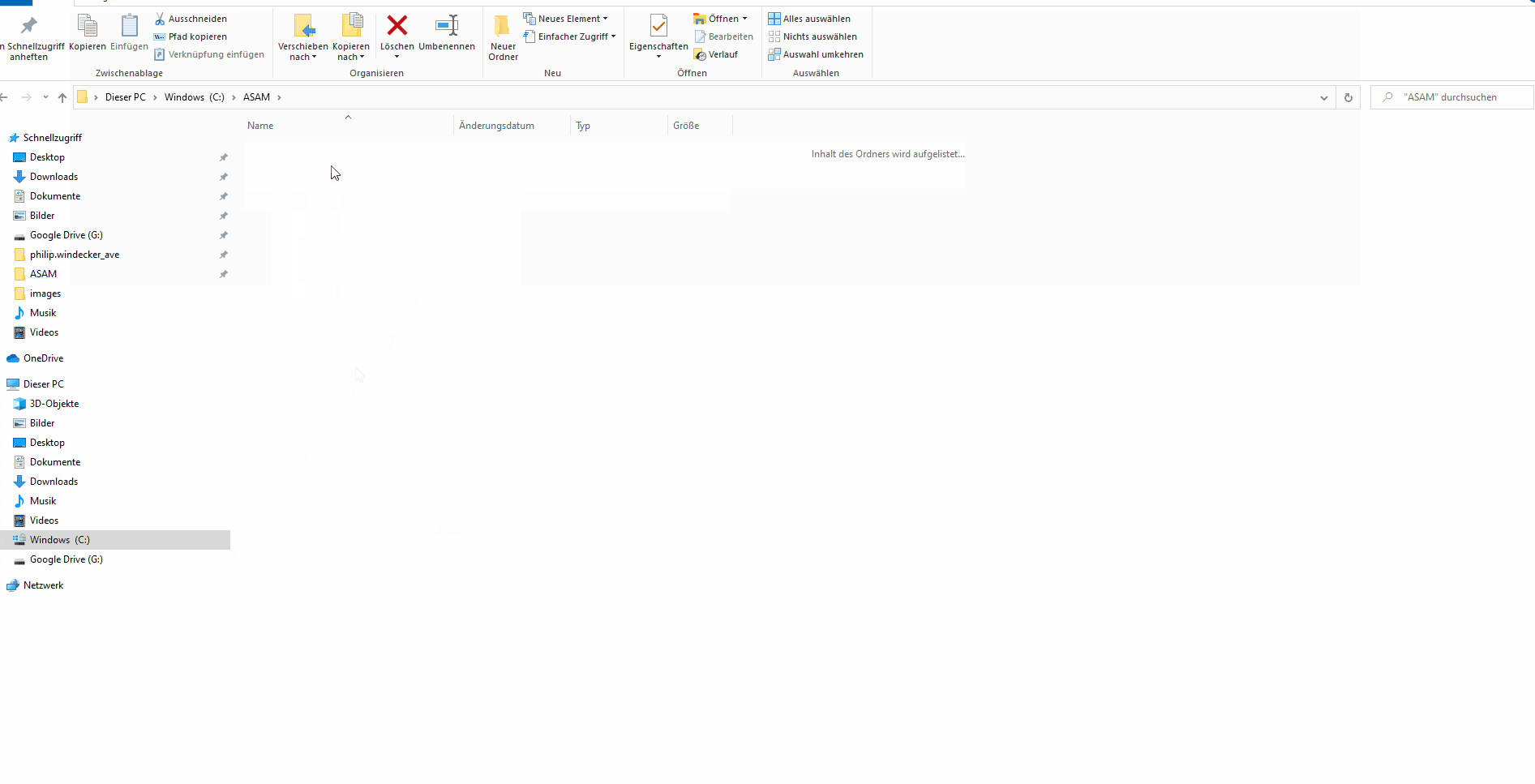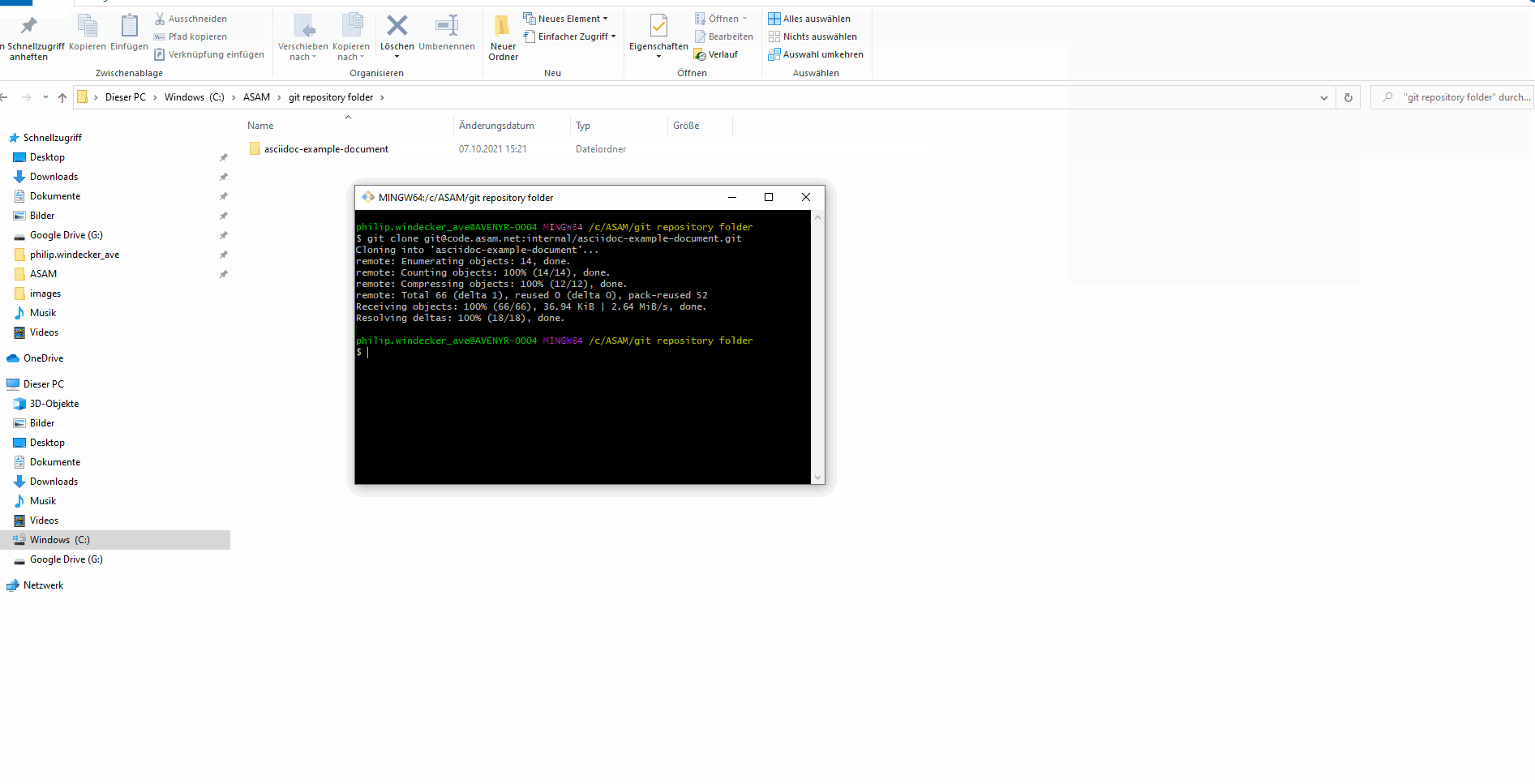
Open the Git Bash from the Context Menu (right-click → Select "Git Bash Here")
-
Type
git clone --recurse-submodulesand then press the middle mouse button to paste the copied url. Confirm with EnterWith this command, you do not need to manually initialize the submodules after checkout!
| Alternatively to the Git Bash, you can also use the terminal with the same commands. Make sure to open your Powershell in your directory, though. |
| This only needs to be done once to obtain a local copy. |
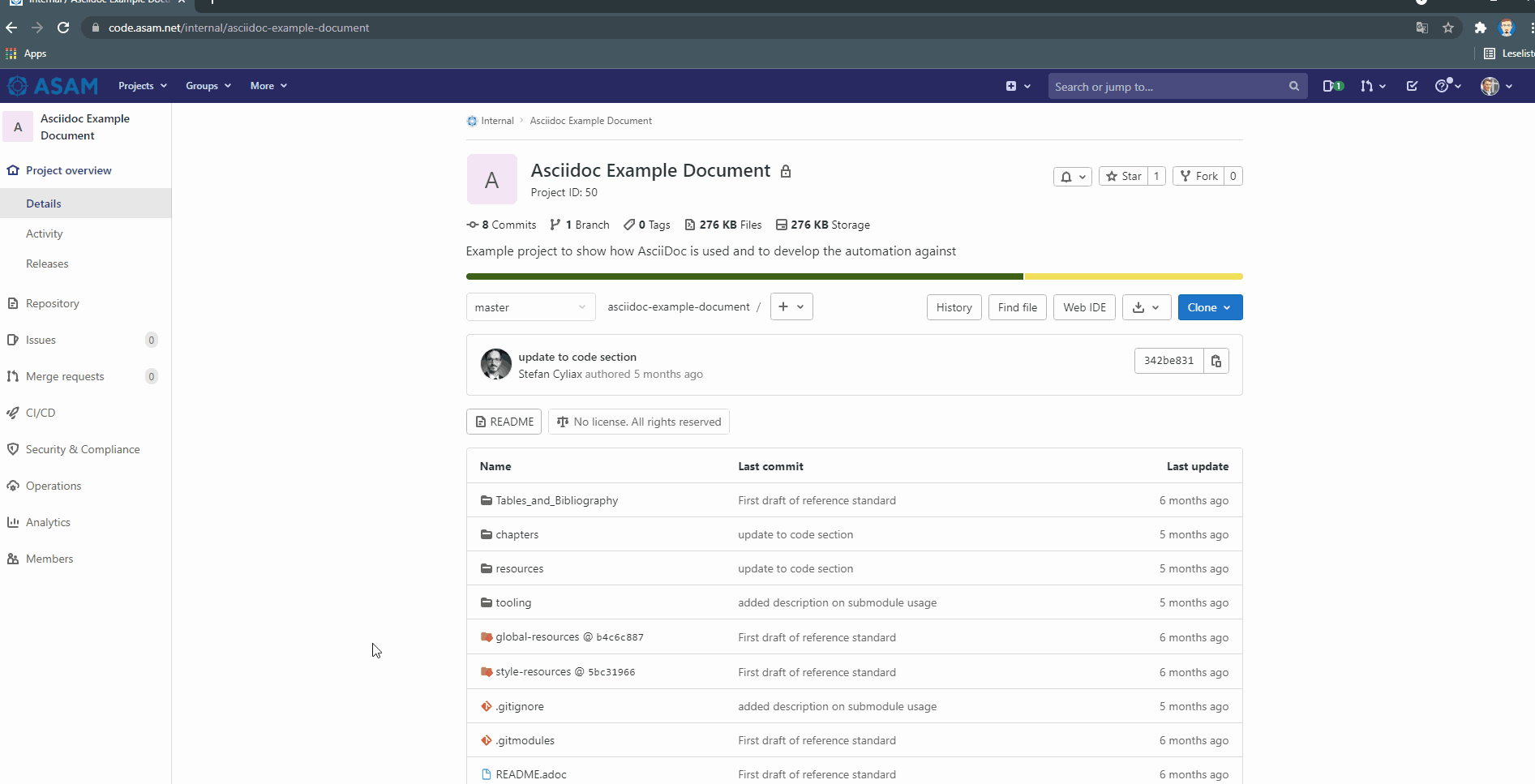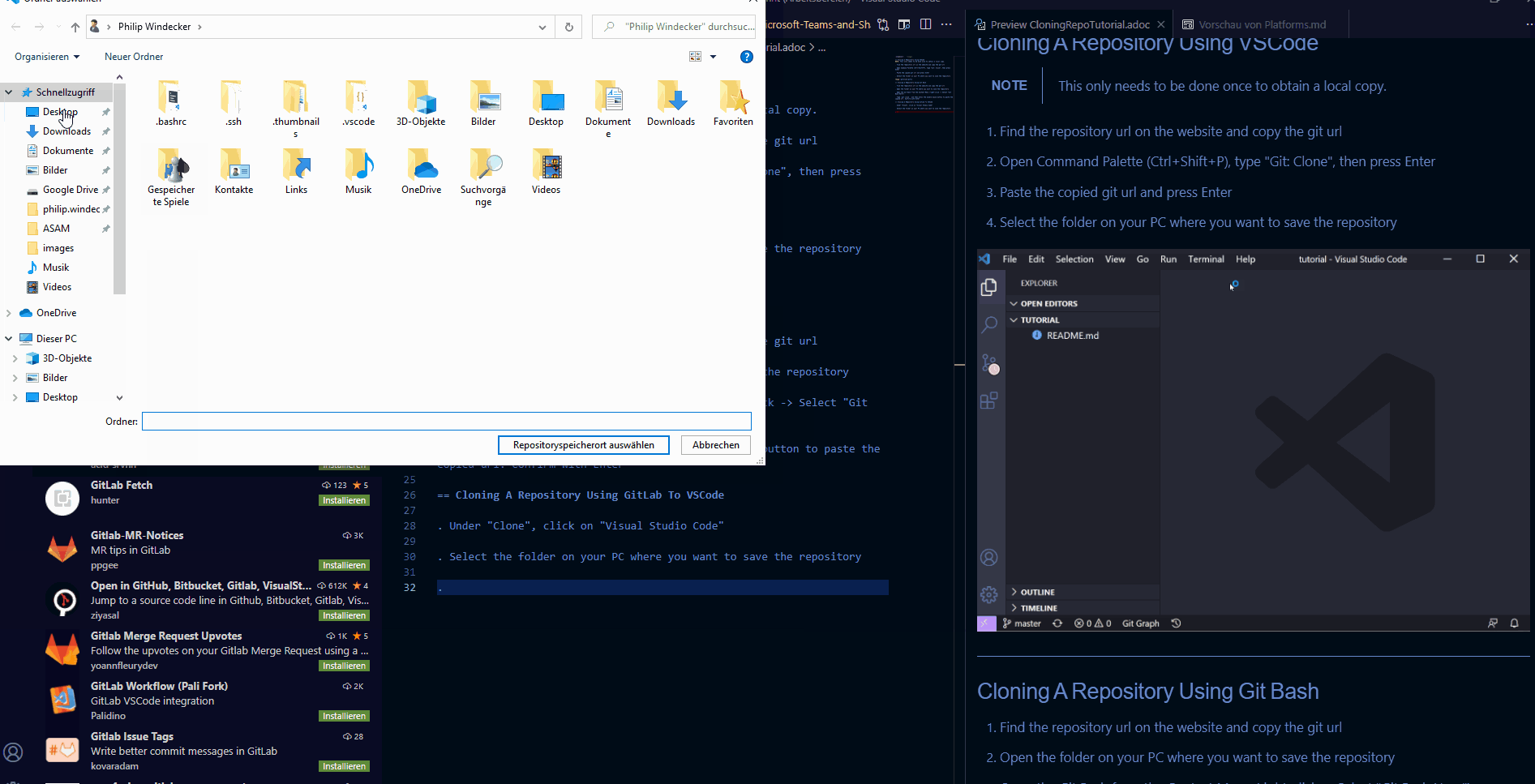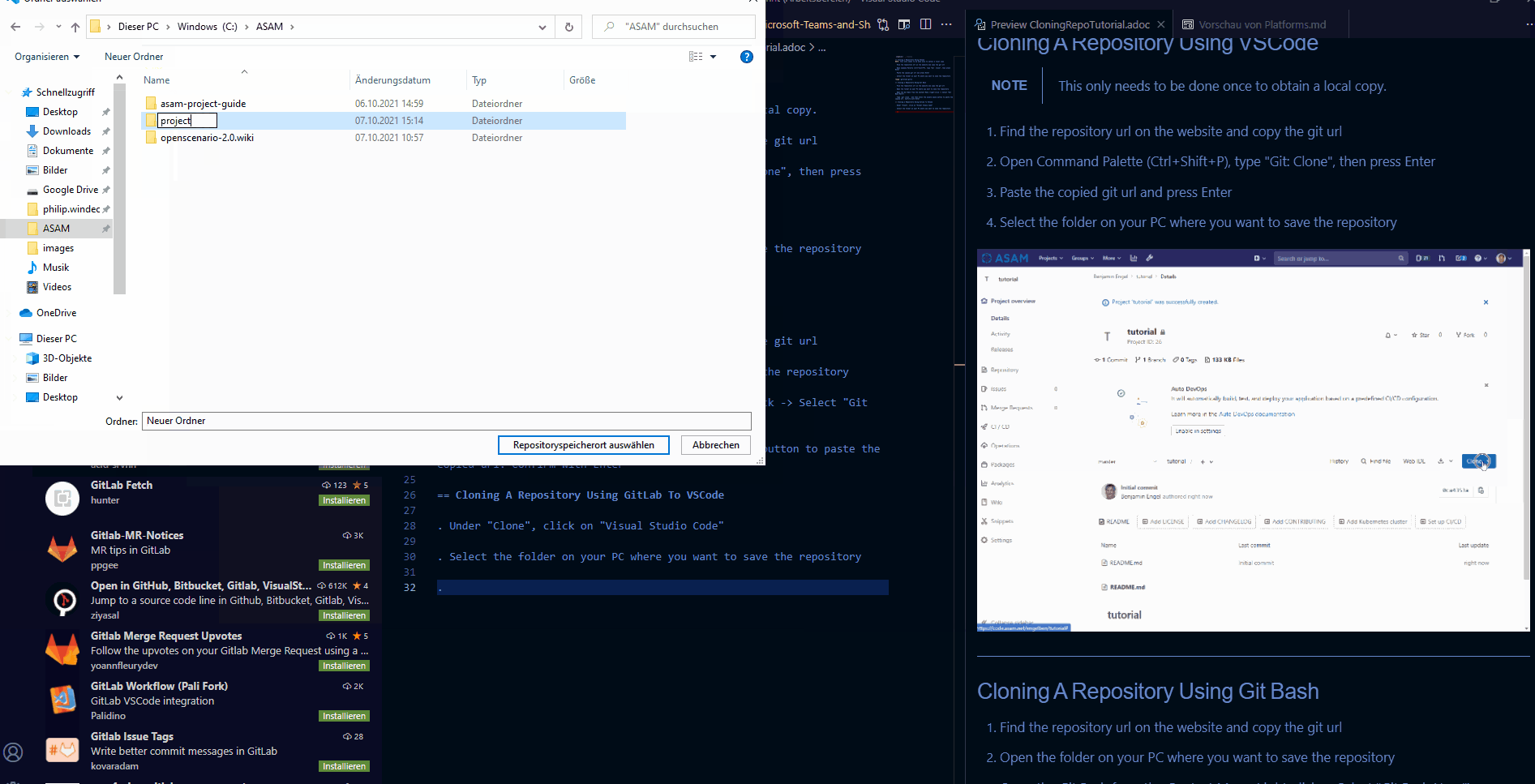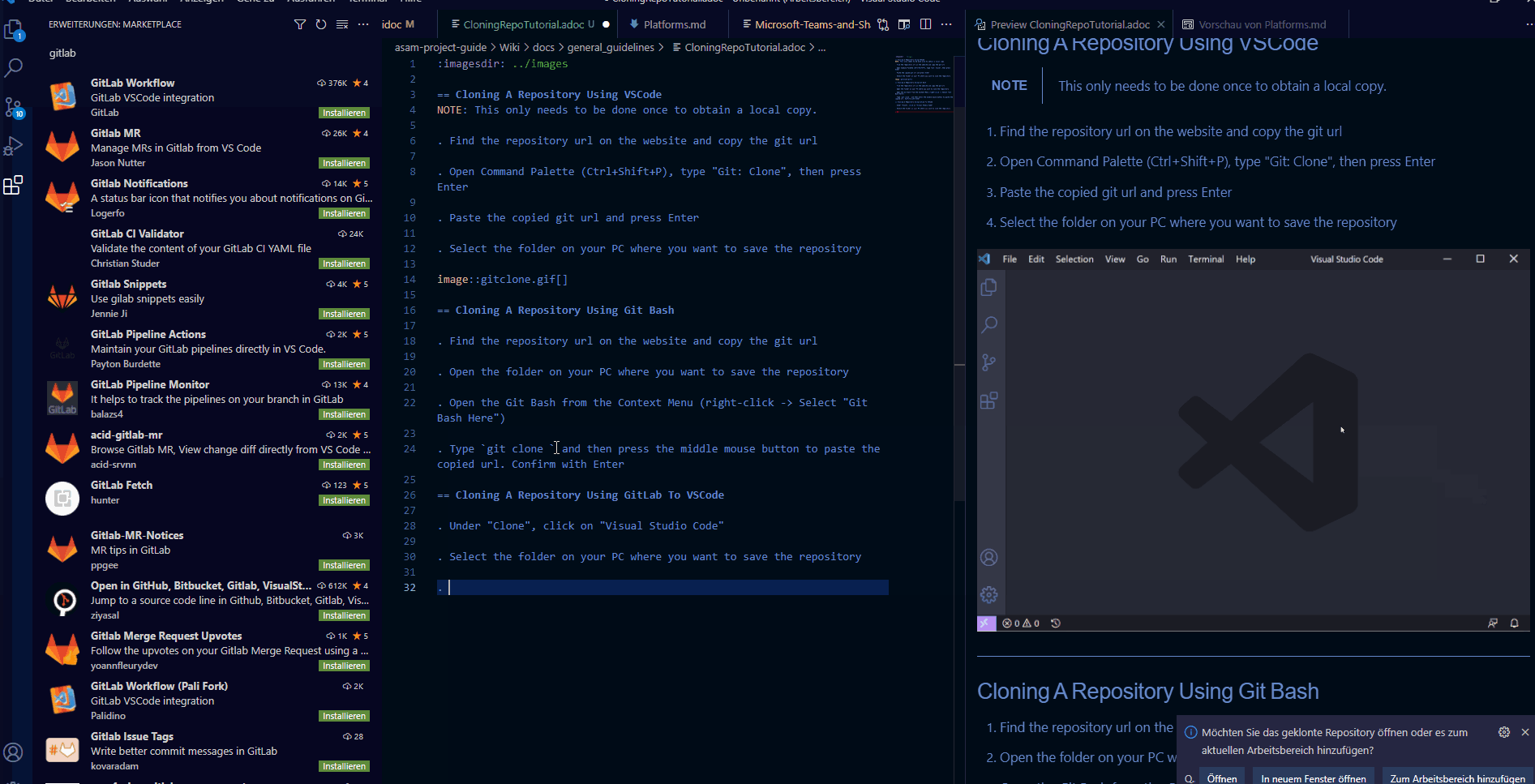
-
Find the repository url on the website and copy the git url
-
Open the Command Pallette (Ctrl+Shift+P), type
Git: Clone, then press Enter -
Paste the copied git url and press Enter
-
Select the folder on your PC where you want to save the repository
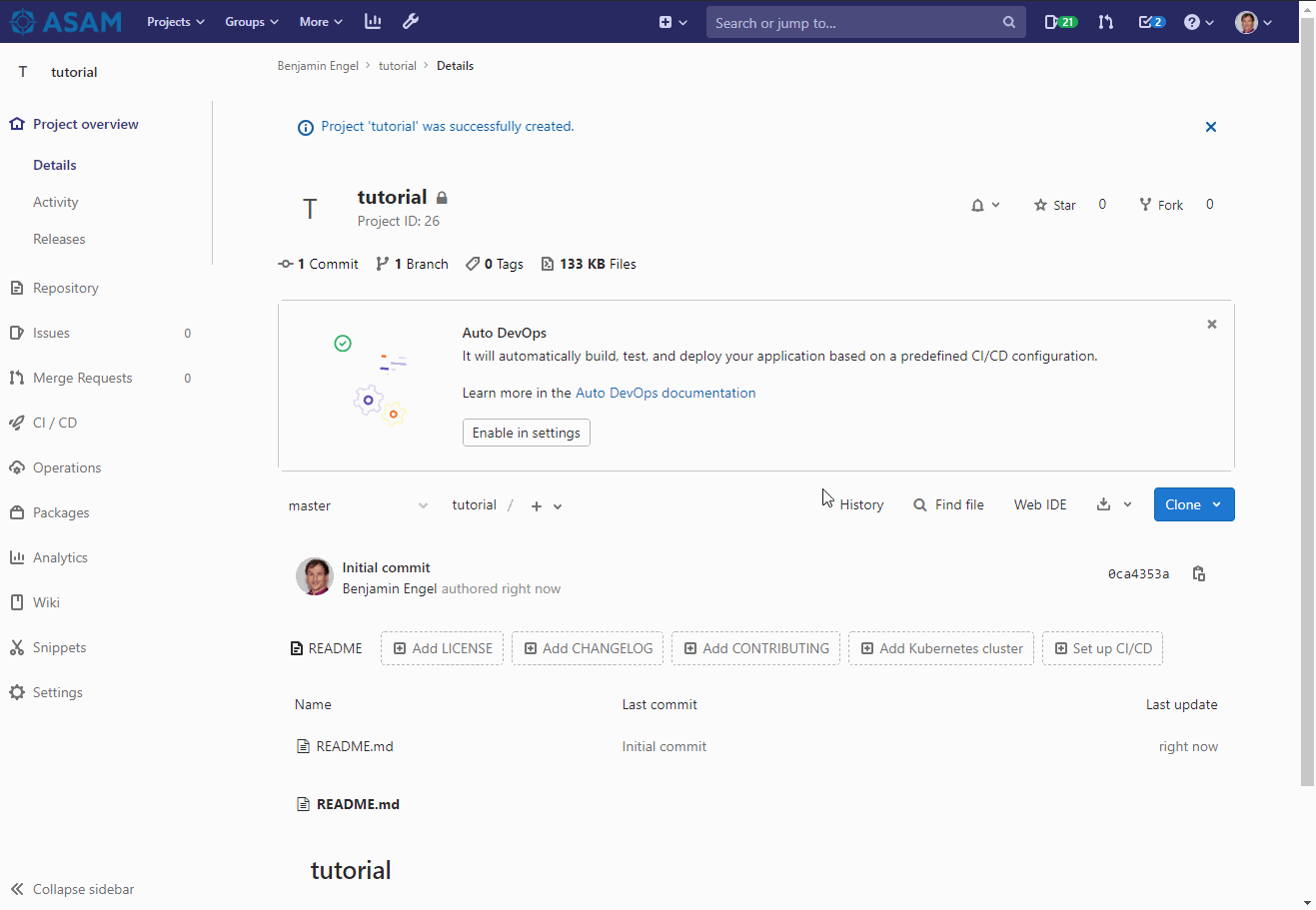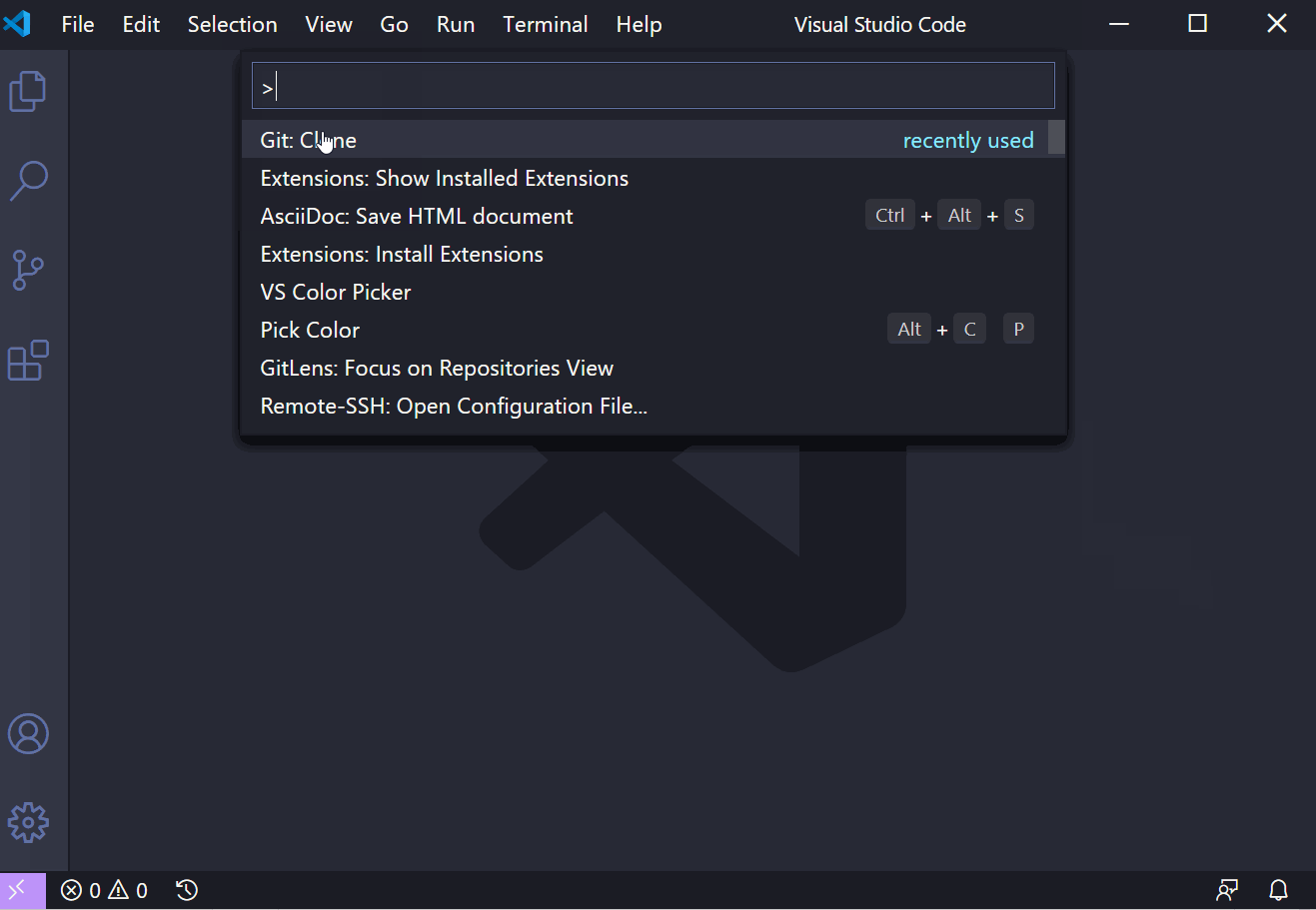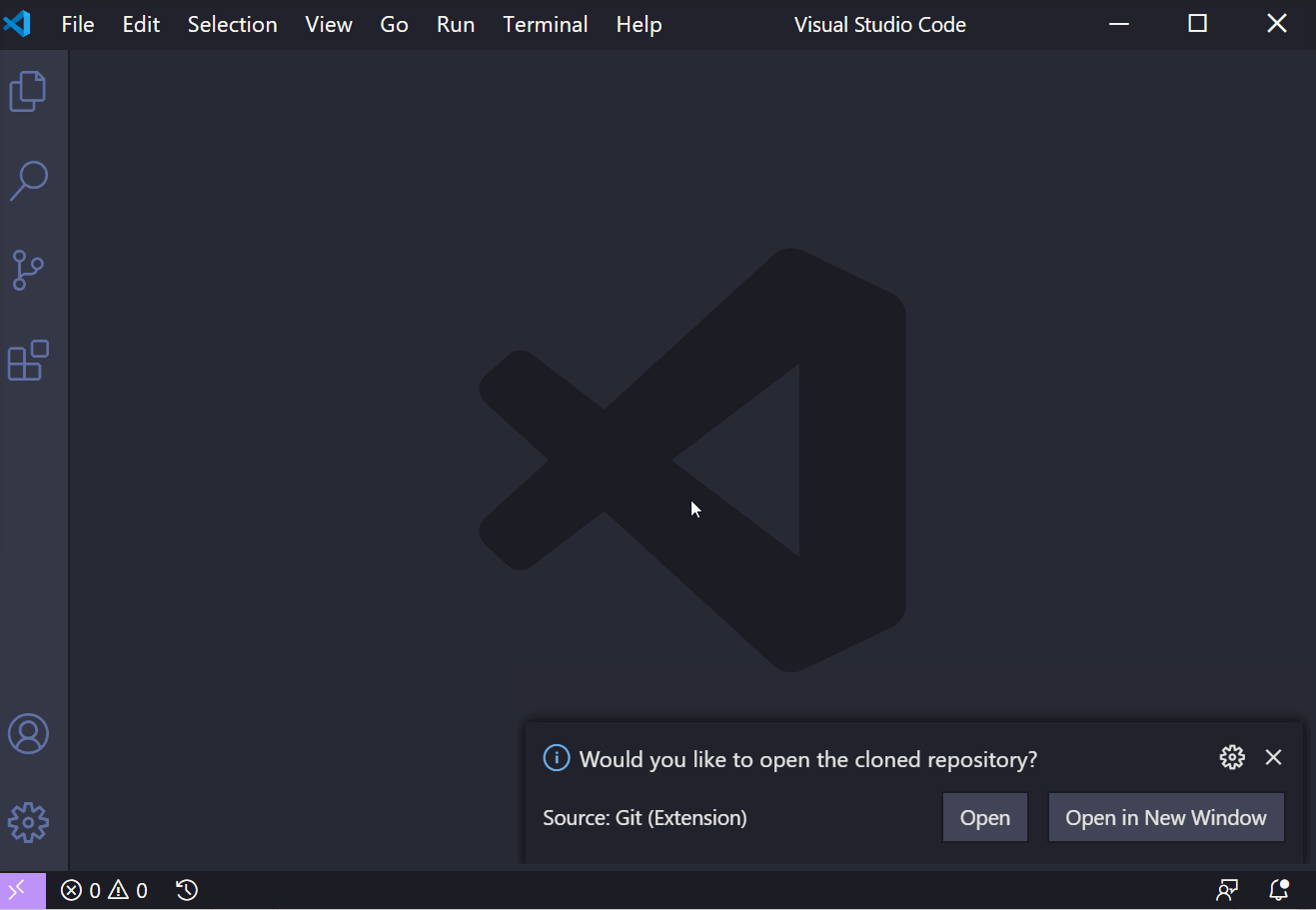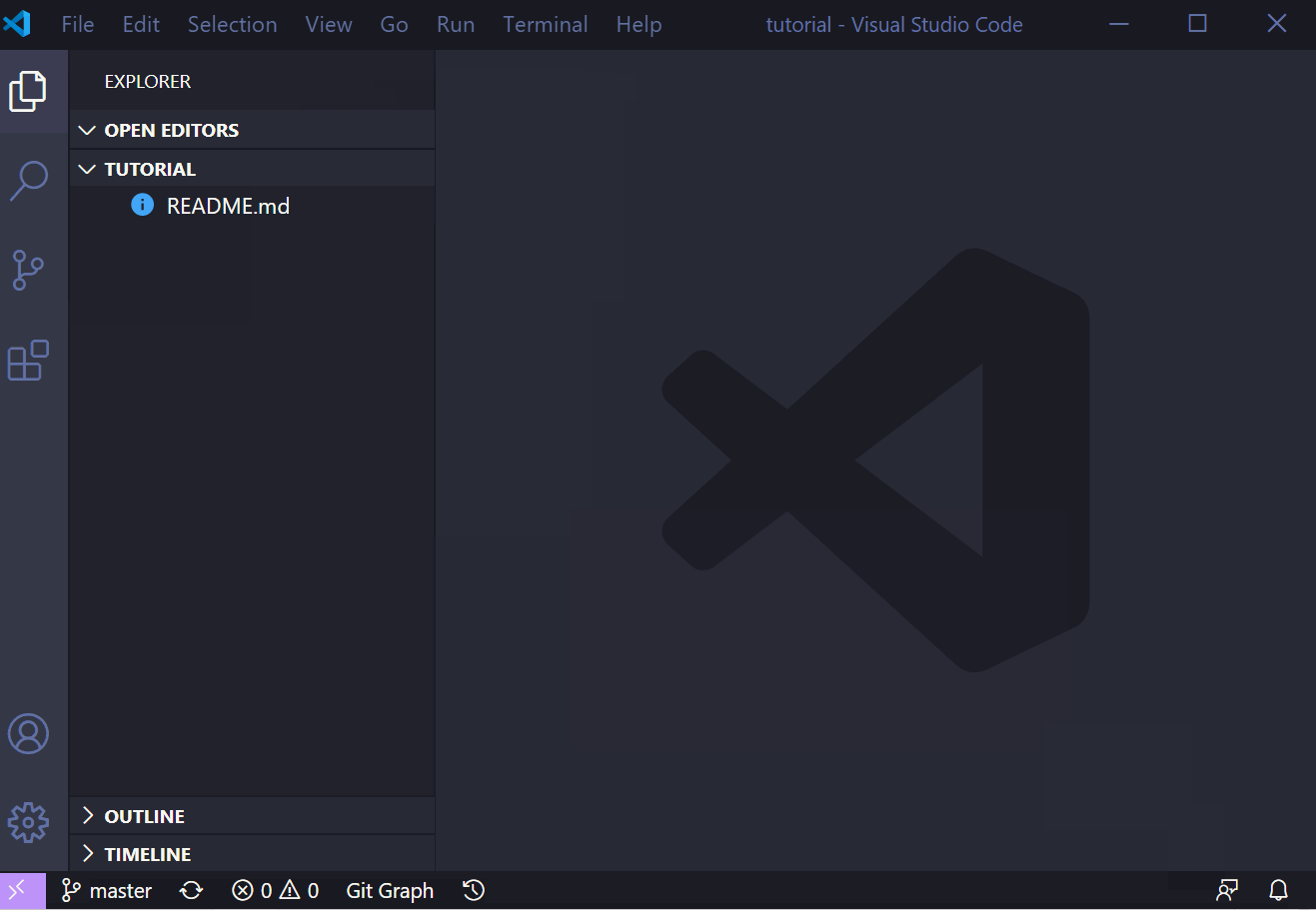
|
If you encounter an error that the host key verification failed, you need to add GitLab to your known_host file. |
-
Click
-
Select the folder on your PC where you want to save the repository